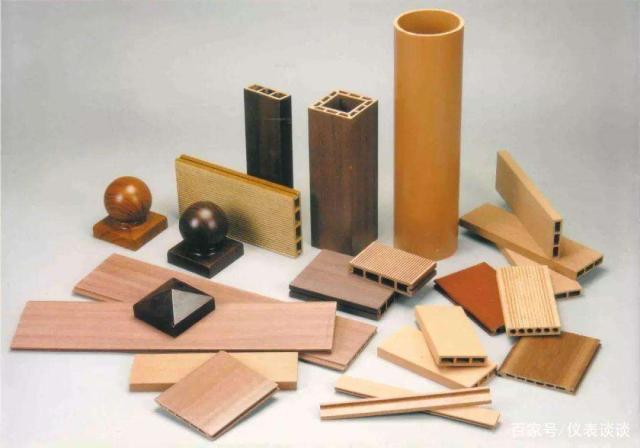
WPC is a composite material formed by using hot melt plastics, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride and their copolymers as adhesives, using wood powder such as wood, agricultural plant straw, agricultural plant shell powder as filling materials, extrusion molding or pressing method, injection molding method. The hot melt plastic raw materials can be used industrial or life waste materials, wood powder can also be used wood processing waste, small wood and other low-quality wood. From the perspective of production of raw materials, wood plastic products slow down and eliminate the pollution of plastic waste, and also eliminate the pollution caused by agricultural plant incineration to the environment. The selection of material formula in the composite process involves the following aspects:

1. Polymers
The plastics used in the processing of wood-plastic composites can be thermoset plastics and thermoplastics, thermoset plastics such as epoxy resins, thermoplastics such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyoxyethylene (PVC). Due to the poor thermal stability of wood fiber, only thermoplastics with processing temperatures below 200 ° C are widely used, especially polyethylene. The selection of plastic polymers is mainly based on the inherent characteristics of the polymer, product needs, raw material availability, cost and the degree of familiarity with it. Such as: polypropylene is mainly used in automotive products and daily life products, PVC is mainly used in building doors and Windows, paving panels and so on. In addition, the melt flow rate (MFI) of the plastic also has a certain impact on the properties of the composite material, under the same processing conditions, the MFI of the resin is higher, the overall infiltration of the wood powder is better, the distribution of the wood powder is more uniform, and the infiltration and distribution of the wood powder affect the mechanical properties of the composite material, especially the impact strength.
2. Additives
Since wood powder has strong water absorption and strong polarity, and most thermoplastics are non-polar and hydrophobic, the compatibility between the two is poor, and the interface bonding force is very small, and appropriate additives are often used to modify the surface of polymer and wood powder to improve the interface affinity between wood powder and resin. Moreover, the dispersion effect of high-filling wood powder in molten thermoplastics is poor, often in a form of aggregation, making the melt flow is poor, extrusion processing is difficult, and surface treatment agents need to be added to improve the flow to facilitate extrusion molding. At the same time, the plastic matrix also needs to add various additives to improve its processing performance and the use of the finished product, improve the binding force between the wood powder and the polymer and the mechanical properties of the composite material. Commonly used additives include the following categories:
a) Coupling agent can produce strong interface bonding between plastic and wood powder surface; At the same time, it can reduce the water absorption of wood powder and improve the compatibility and dispersion of wood powder and plastic, so the mechanical properties of composite materials are significantly improved. Commonly used coupling agents are: isocyanate, isopropylbenzene peroxide, aluminate, phthalates, silane coupling agent, maleic anhydride modified polypropylene (MAN-g-PP), ethylene-acrylate (EAA). Generally, the addition amount of coupling agent is 1wt% ~ 8wt% of the added amount of wood powder, such as silane coupling agent can improve the adhesion of plastic and wood powder, improve the dispersion of wood powder, reduce water absorption, and alkaline treatment of wood powder can only improve the dispersion of wood powder, can not improve the water absorption of wood powder and its adhesion with plastic. It should be noted that the maleate coupling agent and the stearate lubricant will have a repulsive reaction, which will lead to a decrease in product quality and yield when used together.
b) Plasticizer For some resins with high glass transition temperature and melt flow viscosity, such as hardness PVC, it is difficult to process when it is combined with wood powder, and it is often necessary to add plasticizer to improve its processing performance. Plasticizer molecular structure contains polar and non-polar genes, under the action of high temperature shear, it can enter the polymer molecular chain, through the polar genes attract each other to form a uniform and stable system, and its long non-polar molecule insertion weakens the mutual attraction of polymer molecules, so that the processing is easy. Dibutyl phthalate (DOS) and other plasticizers are often added to wood-plastic composites. For example, in the PVC wood powder composite material, the addition of plasticizer DOP can reduce the processing temperature, reduce the decomposition and smoke of wood powder, and improve the tensile strength of the composite material while the elongation at break increases with the increase of the DOP content.
c) Lubricants Wood-plastic composites often need to add lubricants to improve the fluidity of the melt and the surface quality of the extruded products, and the lubricants used are divided into internal lubricants and external lubricants. The choice of internal lubricant is related to the matrix resin used, which must have good compatibility with the resin at high temperature, and produce a certain plasticizing effect, reduce the cohesion energy between molecules in the resin, weaken the mutual friction between molecules, in order to reduce the melt viscosity of the resin and improve the melt fluidity. The external lubricant actually plays the role of interface lubrication between resin and wood powder in plastic molding processing, and its main function is to promote the sliding of resin particles. Usually a lubricant often has both internal and external lubrication properties. Lubricants have a certain impact on the service life of the mold, barrel and screw, the production capacity of the extruder, the energy consumption in the production process, the surface finish of the product and the low temperature impact performance of the profile. Commonly used lubricants are: zinc stearate, ethylene bisfatty acid amide, polyester wax, stearic acid, lead stearate, polyethylene wax, paraffin wax, oxidized polyethylene wax and so on.
d) Colorant In the use of wood-plastic composite materials, the solvable substance in wood powder is easy to migrate to the surface of the product, so that the product decolorization, and eventually become gray, different products in a certain use environment, but also produce black spots or rust spots. Therefore, colorants are also widely used in the production of wood-plastic composite materials. It can make the product have a uniform and stable color, and the decolorization is slow.
e) Foaming agent wood-plastic composite material has many advantages, but due to the composite of resin and wood powder, its ductility and impact resistance are reduced, the material is brittle, and the density is nearly 2 times larger than that of traditional wood products, limiting its wide use. Due to the good bubble structure, the foamed wood-plastic composite can passivate the crack tip and effectively prevent the expansion of the crack, thus significantly improving the impact resistance and ductility of the material, and greatly reducing the density of the product. There are many types of blowing agents, and there are mainly two commonly used: endothermic blowing agents (such as sodium bicarbonate NaHCO3) and exothermic blowing agents (azodibonamide AC), whose thermal decomposition behavior is different, and have different effects on the viscoelasticity and foaming form of polymer melt, so the appropriate blowing agent should be selected according to the requirements of the use of products.
f) The application of UV stabilizers and other UV stabilizers has also developed rapidly with the improvement of people’s requirements for the quality and durability of wood-plastic composites. It can make the polymer in the composite material does not degrade or mechanical properties decline. Commonly used are blocked amine light stabilizers and ultraviolet absorbers. In addition, in order to make the composite material can maintain a good appearance and perfect performance, it is often necessary to add antibacterial agents, and the selection of antibacterial agents should consider the type of wood powder, the amount of addition, the bacteria in the composite material use environment, the water content of the product and other factors. Zinc borate, for example, is preservative but not algal.
The production and use of wood-plastic composite materials will not emit volatiles harmful to human health to the surrounding environment, and the wood-plastic products themselves can be recycled and reused, so the wood-plastic products are a new kind of green environmental protection products, which can be ecological self-cleaning and have broad development prospects
Post time: Jun-24-2023